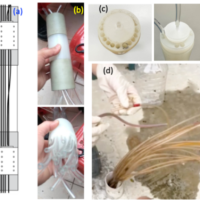
Multi-Depth Monitoring Systems
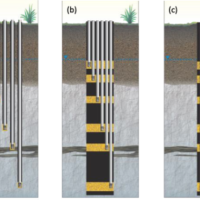
Summary: This document provides a comprehensive technical overview of Multi-Depth Systems (MDS) and their transformative role in modern groundwater science. It begins by establishing the critical need for high-resolution vertical profiling to capture subsurface heterogeneity—something conventional single-screen wells fundamentally obscure. The text details the evolution, design, and comparative advantages of five major MDS technologies (Westbay, Waterloo, WaterFlute, CMT, and HKU), highlighting the HKU system’s innovations: low-cost 3D-printed components, the revolutionary HKUniversal seal that expands on contact with water, and compatibility with miniature sensors to maximize port density. These features make the HKU-DHS not only scientifically superior but also globally accessible and adaptable to diverse geological settings, from fractured rock to coastal aquifers.
Beyond hardware, the document underscores why MDS data is indispensable. Through compelling case studies—from redefining aquitards in Wisconsin and tracing 9,000-year-old paleo-seawater in China to mapping nested flow systems on the Ordos Plateau and exposing geochemical heterogeneity in submarine groundwater discharge—the text demonstrates how depth-discrete data resolves ambiguities, corrects flawed conceptual models, and reveals hidden hydrogeological processes. MDS is presented not as a luxury, but as a necessity for accurate risk assessment, effective remediation, and defensible water resource management. The document concludes that recent advances, particularly the affordable and open-source HKU-DHS, have removed cost and complexity barriers, democratizing high-resolution groundwater characterization for researchers, practitioners, and educators worldwide. [Read more]
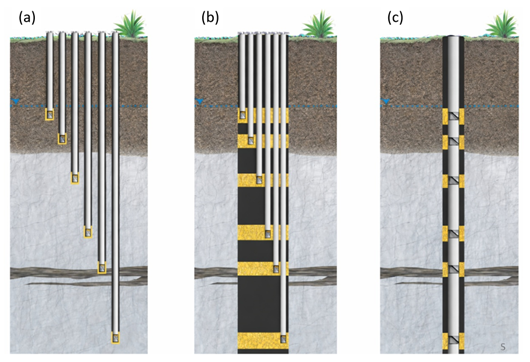
Summary: The HKU Depthwise HydrogeoSystem (HKU-DHS) is a groundbreaking suite of low-cost, high-resolution groundwater monitoring technologies developed by the University of Hong Kong in collaboration with The Groundwater Project. Designed to overcome the limitations of conventional single-depth monitoring, HKU-DHS enables precise, depth-discrete measurements of hydraulic head and water chemistry across diverse hydrogeological settings — from porous aquifers to fractured rock and coastal zones. Leveraging 3D-printed components and an innovative HKUniversal seal, the system is affordable, adaptable, and easy to deploy locally worldwide. With eight distinct configurations tailored for applications ranging from contaminant tracking and saltwater intrusion monitoring to urban hydrology and mining, HKU-DHS democratizes access to critical subsurface data. Released as an open-source initiative, it empowers researchers, practitioners, and educators to generate field-relevant, high-resolution datasets — filling a crucial gap in groundwater science and supporting evidence-based water resource management globally. [Read more]
3) Resources
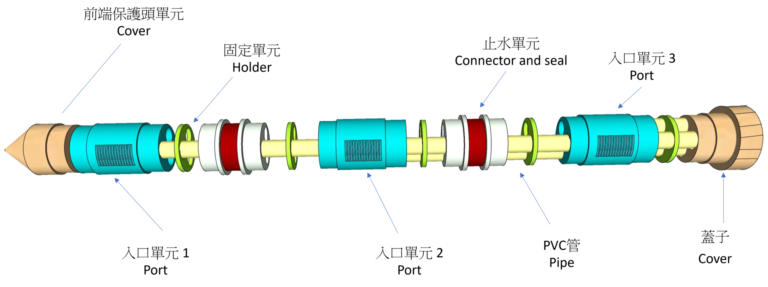
3.1) Brief Introduction of HKU-MDS (Dual Purpose System)
3.2) Case study
3.3) Papers about or based on HKU-DHS
- Liang, W., Jiao, J.J., Liu, Y., Yu, S., Ho, K.B.E., Luo, X., Cherry, J.A., 2025. Breaking the Technical Barrier for High Spatial Resolution Monitoring: A Novel Approach to Multi-Level Groundwater Monitoring System Development. ACS EST Water 5, 2343–2351.
- Yu, S., Jiao, J.J., Luo, X., Wang, X., Zuo, J., Liang, W., Lu, M., Li, H., 2025. Characterisation of Groundwater Flow in the Deltaic Aquifer-Aquitard System. Hydrological Processes 39, e70255.
- Cheng, K.H., Luo, X., Jiao, J.J., Yu, S., 2023. Storm accelerated subsurface Escherichia coli growth and exports to coastal waters. Journal of Hazardous Materials 441, 129893.
- Liu, Y., Jiao, J.J., Mao, R., Luo, X., Liang, W., Robinson, C.E., 2019. Spatial Characteristics Reveal the Reactive Transport of Radium Isotopes (224 Ra,223 Ra, and228 Ra) in an Intertidal Aquifer. Water Resources Research 55, 10282–10302.
- Luo, X., Kwok, K.L., Liu, Y., Jiao, J., 2017. A Permanent Multilevel Monitoring and Sampling System in the Coastal Groundwater Mixing Zones. Groundwater 55, 577–587.
- Yu, S., Jiao, J.J., Liu, Y., Luo, M., Li, H., 2024. Occurrence of CO2 and CH4 and the behavior of inorganic carbon in the groundwater of the Pearl River Delta. Science of The Total Environment 956, 177141.
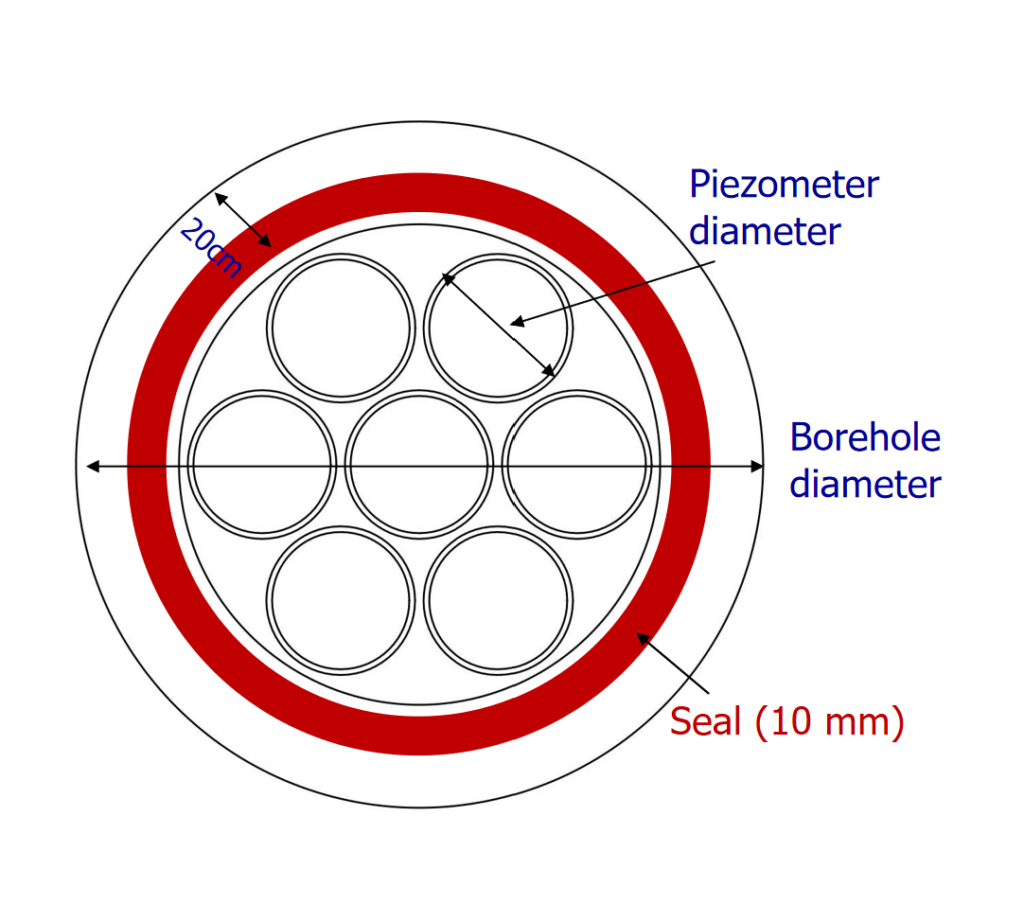
3.4) Estimation of number of piezometers in HKU Dual Purpose System
Contact us
If you are interested in this system or have any further questions, please feel free to contact Mr. Jinchao Zuo (jczuo@connect.hku.hk) or Ms. Tao Yang (taoy@connect.hku.hk).